In a world where resource scarcity and environmental concerns loom large, the circular economy has emerged as a transformative approach to business and sustainability. This article explores the concept of the circular economy and the innovative business models driving its adoption, ushering in a more sustainable and resilient future.
Understanding the Circular Economy
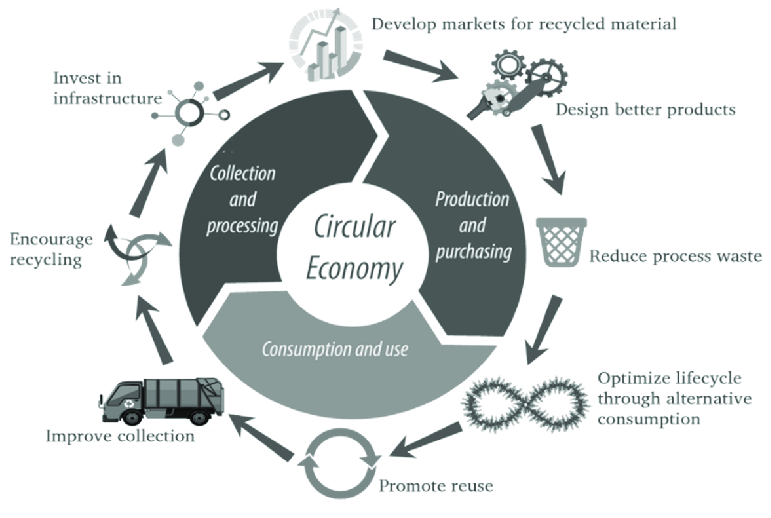
The traditional linear economy model follows a “take, make, ceocolumn dispose” pattern. Resources are extracted, products are manufactured, used, and eventually discarded as waste. This linear approach is unsustainable, leading to resource depletion and environmental degradation. In contrast, the circular economy seeks to close the loop, keeping products and materials in use for as long as possible through recycling, reuse, and responsible resource management.
Key Principles of the Circular Economy
- Design for Sustainability: Circular businesses prioritize product design that maximizes durability, repairability, and recyclability. Products are engineered to have longer lifespans and ease of disassembly.
- Resource Efficiency: Efficient use of resources is paramount. Companies aim to minimize waste, energy consumption, and raw material usage throughout the product lifecycle.
- Reuse and Refurbishment: Rather than discarding products, the circular economy promotes the repair, refurbishment, and resale of goods. This extends their lifespan and reduces waste.
- Recycling and Upcycling: Materials are collected and recycled into new products or upgraded into higher-value materials. This conserves resources and reduces the environmental impact of production.
- Sharing and Collaborative Consumption: Sharing platforms and collaborative consumption models encourage individuals and businesses to share access to products and services, reducing the need for individual ownership.
- Reverse Logistics: Circular TheTechFixr businesses implement efficient systems for product return, remanufacturing, and recycling at the end of a product’s life.
Innovative Business Models
Several innovative business models have emerged within the circular economy framework:
- Product-as-a-Service (PaaS): Companies offer products on a subscription or lease basis instead of selling them outright. This encourages manufacturers to design for durability and provides a continuous revenue stream while reducing waste.
- Sharing Platforms: Ride-sharing, accommodation-sharing, and coworking platforms exemplify the sharing economy. These platforms maximize the use of existing resources and reduce the need for ownership.
- Remanufacturing: Companies like Xerox and Caterpillar remanufacture used products to “like-new” condition, extending their life and reducing the demand for new replacements.
- Closed-Loop Supply Chains: Businesses establish systems for collecting and reusing materials from their own products. For example, textile companies recover and recycle fibers from old clothing.
- Circular Design Consultancies: Consultants help businesses redesign their products and processes with circular principles in mind, ensuring sustainable practices from the start.
Benefits of the Circular Economy
The circular economy offers a range of benefits:
- Resource Conservation: It reduces the need for virgin resources, preserving natural ecosystems and reducing environmental impact.
- Waste Reduction: Waste generation is minimized, reducing landfill usage and pollution.
- Cost Savings: Businesses can save money through reduced material costs, efficient processes, and extended product lifecycles.
- Job Creation: New business models and industries within the circular economy create job opportunities.
- Resilience: A circular economy is more resilient to resource shortages and price fluctuations.
Global Impact and Challenges
The circular economy is gaining momentum globally, with SettingAid governments, businesses, and consumers recognizing its potential. However, challenges remain, such as transitioning from linear business models, overcoming regulatory barriers, and scaling circular practices across industries.
Conclusion
The circular economy is not just a sustainable vision; it’s a practical and necessary shift in our approach to resources and business. Innovative models that prioritize resource efficiency, waste reduction, and environmental responsibility are at the forefront of this transformation. As we embrace the circular economy, we move closer to a sustainable future where economic growth and environmental protection go hand in hand.